Ask for a reprint
email :
* Give your email
2019
ACL
|
Maria C.Fernandez de Cordoba, Juan Matos, Ricmary Montaña, Po S.Poon, Silvania Lanfredi, Fabiano R.Praxedes, Juan C.Hernández-Garrido, José J.Calvino, Elena Rodríguez-Aguado, Enrique Rodríguez-Castellón, Conchi O.Ania, 'Sunlight photoactivity of rice husks-derived biogenic silica', Catal. Today 328 125-135 (2019) doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2018.12.008
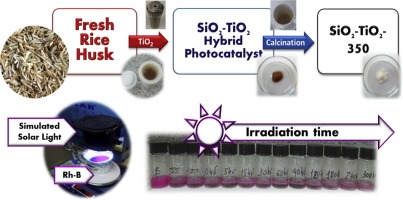
Carbon-containing SiO2-based photocatalysts were prepared by the solvothermal treatment of rice husk as biogenic precursor in the presence and absence of TiO2 and used for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B under simulated solar light. Data showed that the prepared catalysts are mainly composed of biogenic silica and displayed mesoporous character with surface areas ranging from 65 to 174 m2 g-1. The obtained materials showed photocatalytic activity comparable to that of commercial TiO2-P25 powders for the degradation of rhodamine-B under sunlight. The calcination at 350 °C improved the photocatalytic activity of the biogenic precursor by three times in the absence of TiO2. At converse, calcination of sample SiO2-TiO2 decreased the photoactivity due to the appearance of non-photoactive TiSiO4 crystalline phases in the catalyst, as inferred by XRD and XPS. A reaction mechanism for rhodamine-B degradation excluding the deethylation pathway has been proposed, based on the evolution of the absorbance spectra of rhodamine-B upon the photocatalytic tests.
|
|