Ask for a reprint
email :
* Give your email
2018
ACL
|
A.A.Kulbakov, A.B.Kuriganova, M.Allix, A.Rakhmatullin, N.V.Smirnova, O.A.Maslova, I.N.Leontyev, 'Non-isothermal decomposition of platinum acetylacetonate as a new cost-efficient and Size-Controlled Synthesis of Pt/C nanoparticles', Catal. Commun. 117 14-18 (2018) doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2018.08.022
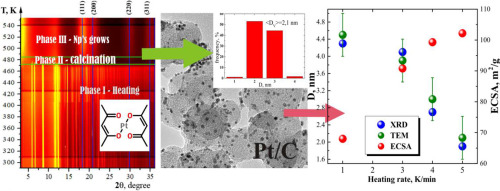
The thermal decomposition of platinum acetylacetonate and platinum nanoparticles forming upon the decomposition are studied in-situ via X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy, termal gravimetric analisys, scanning (SEM) and transmition electronic microscopy (TEM). The experiments are made at the rates of heatings of 1 and 5 K/min. The comprehensive analysis of SEM, TEM and XRD data evidences the formation of coarse Pt particles upon the thermal decomposition, whose sizes vary as ~60--160 nm, and which are in turn composed of nanoparticles with dimensions of 1.9 and 4.1 nm for 1- K/min- and 5 K/min-rates of heating, respectively. This means that the desirable average size of nanoparticles during theirs synthesis can be achieved through a simple tuning of the rate of heating of acetylacetate thermal decomposition.
|
|