Ask for a reprint
email :
* Give your email
2006
ACLN
|
H.Gomart, S.Schelz, E.Véron, B.Rousseau, P.Echegut, 'Effect of the Scattering of Light on the Thermal Radiative Properties of a Nearly Black Body Coating', Sixteenth symposium on thermophysical properties, Boulder, CO, USA, July 30 - August 4 (2006)
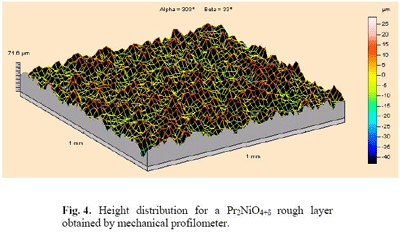
Black body coatings can be elaborated by depositing a rough layer of Pr2NiO4+δ, onto a ceramic substrate. Two complementary effects can be underlined when one investigates the physical basis explaining such a remarkable behaviour. The first one lies in the oxygen excess (+δ), creating polaronic carriers that are responsible for the intrinsic absorption mechanism in the infrared range. It makes the deposit opaque when the thickness is superior to 2.5 μm. The second one involves the roughness of the layer that is due to the chemical deposit process. To get a more quantitative evaluation of this second effect, we carry out a Monte Carlo Ray Tracing program acting in a virtual reconstruction of the layer. Our aim is to reproduce the normal spectral emittance of the layer, for which experimental measurement has been done at different temperatures.
|
|