Ask for a reprint
email :
* Give your email
2011
ACL
|
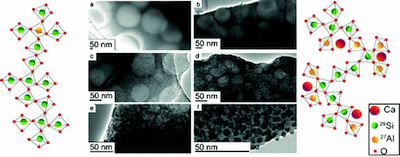
L.Martel, M.Allix, F.Millot, V.Sarou-Kanian, E.Véron, S.Ory, D.Massiot, M.Deschamps, 'Controlling the size of nanodomains in calcium aluminosilicate glasses', J. Phys. Chem. C 115 18935–18945 (2011) doi:10.1021/jp200824m
Transparent nanostructured glasses show interesting properties for optical fibers or laser beam applications. Binary calcium silicate glasses are known to undergo phase separation in silica-rich compositions. However, adding up to a few mole percent of alumina seems to inhibit the phase separation. By adjusting the amount of alumina added to demixing calcium silicate glasses, we managed to obtain transparent, but nanostructured, glasses with either silica-rich or calcium aluminosilicate-rich nanodomains of a controlled size down to 5 nm for compositions beyond the limits of the immiscibility domain. Therefore, the limits of the immiscibility domain of the SiO2-Al2O3-CaO ternary diagram must be extended to consider the presence of nanosized domains. An atomic-scale analysis of these glasses was performed using 29Si and 27Al nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments, showing that, as the size of the domains decreased, repolymerization of the silicon network and formation of aluminum-rich clusters were observed.
|
|